Understanding Helicopter's Engine Faults

Servicing helicopter engines demands specialized expertise due to their critical and intricate nature. To ensure smooth and efficient operations, it is crucial for pilots and owners to possess a comprehensive understanding of common faults and how to effectively address them. The persistence of these issues can significantly impact helicopter performance and create operational challenges. In response, we have compiled a curated list of the most frequently encountered faults, drawing upon our extensive field experience. Our comprehensive overview includes a detailed examination of each fault, including their root causes, prominent symptoms, and recommended solutions. Armed with this knowledge, you can approach your next flight with confidence, knowing that you are equipped to navigate any potential challenges and enjoy a seamless and comfortable journey.
The most frequently encountered and persistent helicopter engines problems
Here is a list of the most common faults that our customers frequently ask about.
Engine leaks after the engine wash
This particular issue that commonly arises is engine leaks. This problem typically occurs when the mechanics overlook the proper closure of the stub pipe, leading to leaks within the engine. Consequently, there is a loss of air and an increase of the temperature of exhaust gases. This situation is indicated by sudden decreases in MGT Margin (Maximum Gas Temperature) or TQ Margin (Torque). To resolve this issue, pilots and owners should inspect the engine for air leakage and conduct supplementary tests to determine if adjustments are effective.
Other engine leaks or on the airframe’s side
Another type of engine leak occurs when fuel nozzles are improperly installed resulting in heat losses. Diagnosis of this issue can be done by observing a noticeable decrease in MGT Margin (Maximum Gas Temperature Margin) and Ng Margin (Gas Generator Speed Margin) indicators. The changes observed in these indicators will be smaller compared to the previous example. To address this problem, it is recommended to inspect the engine for air leakage. Additionally, temporarily disabling the air intake for other systems and conducting re-tests can provide valuable insights for potential solutions.
Minimised air intake vent performance
Air intake vent restrictions are commonly attributed to external contaminants entering the vent, often due to the absence of filters. This issue becomes evident through a decrease in Margin MGT and Margin Ng indicators, although less significant than in the case of leaks. To address this problem, an inspection of the engine's intake vents is necessary, including an assessment of filter blockage, air-tightness and proper functioning of the air intake shut-off systems. Once these steps are completed, a final examination is performed by closing the air sluice valve to ensure optimal operation. It is essential to address air intake vent restrictions promptly to maintain engine efficiency and prevent further complications.

Unclean compressor or diffuser
Contaminants can also accumulate and adhere to the compressor blades or within the diffuser, leading to problems in maintaining the required pressure levels at specific speeds within the combustion chamber inlet. When the compressor or diffuser becomes dirty, helicopter engines compensate for losses by increasing energy output, resulting in higher engine speeds to achieve the desired inlet pressure.
Detecting these issues involves observing a consistent decline in Margin MGT and Margin Ng, distinguishing them from previously mentioned faults. Fortunately, regular engine inspections can easily identify and address this problem. However, if monitoring is not frequent, it may be overlooked or mistaken for other issues. Implementing regeneration cleaning techniques can be beneficial, followed by a power check to ensure optimal performance and peace of mind.
Erosion of the compressor or diffuser blades
If the previous checks didn’t provide a solution, the environment in which you operate your helicopter could be causing the erosion of the compressor or diffuser blades. The best way to check if this is the case is to use a borescope. Analyse the operation profile and changes within it frequently and install dust filters as necessary.
Compressor damage due to FOD (Foreign Object Damage)
If MGT Margin and Ng Margin parameters decrease rapidly, it is possible that the engine is experiencing reduced compressor power caused by the ingestion of foreign objects. To address this issue, it is recommended to use a borescope to assess the extent of the damage and undertake necessary repairs to rectify the situation.
Hot section
The combustion chamber is responsible for generating significant energy within the engine. However, if a problem occurs in the hot section, the turbine may not be able to provide sufficient power to the impeller, resulting in decreased power levels. To compensate for these losses, the engine attempts to generate excessive energy, leading to increased fuel consumption.
By closely monitoring indicators such as Ng Margin and MGT Margin, we can quickly identify symptoms of decreased rotation speed and increased exhaust gas temperature, which are early warning signs of potential issues in the hot section. Taking timely action based on these indicators is crucial to prevent further complications.
If the MGT Margin parameter drops below zero, it signifies a severe problem in the engine, the engine is no longer serviceable and needs to be fixed immediately. In such cases, immediate repairs are essential to restore the engine's functionality and ensure its safe operation.
Most frequent faults in the hot section
- Compressor turbine stator vane burning – this is usually caused by an unclean fuel nozzle. You may see increases in both MGT and fuel consumption
- Increase of compressor turbine blade tip clearance – is often observed as engines are used over time. Factors such as rubbing or overheating can contribute to reduced clearance between the turbine blades and the engine channel. This can result in substantial power losses as hot air escapes between the blades and the sides of the engine channel. Additionally, this fault leads to higher MGT (exhaust gas temperature) and increased fuel consumption, while the rotation speed of the turbine decreases. Monitoring and addressing the tip clearance is vital to maintain optimal engine performance. Regular inspections and maintenance can help identify and rectify any issues related to turbine blade tip clearance, ensuring efficient power output and fuel utilization.
- Erosion of the compressor’s turbine blades – is often a result of exposure to polluted air, particularly containing sulphur. This erosion leads to a decrease in the turbine's performance, which can be identified by observed increases in MGT (exhaust gas temperature) and fuel consumption. Polluted air containing sulphur compounds can cause accelerated wear and damage to the turbine blades, affecting their aerodynamic efficiency. Regular inspections and maintenance are crucial to detect and address any erosion-related issues promptly. By mitigating the effects of erosion, the engine's overall performance and fuel efficiency can be preserved, ensuring optimal operation in the long run.
Solving issues regarding the hot section
In order to minimize and address faults in the hot section of the engine, regular monitoring of the engine's technical condition is crucial. When a problem arises, it can typically be resolved through the following steps:
- Borescope checks
- Increased intervals between regenerative cleaning
- Fuel nozzle replacement
- Changes in helicopter use (restricting quick starts, for example)
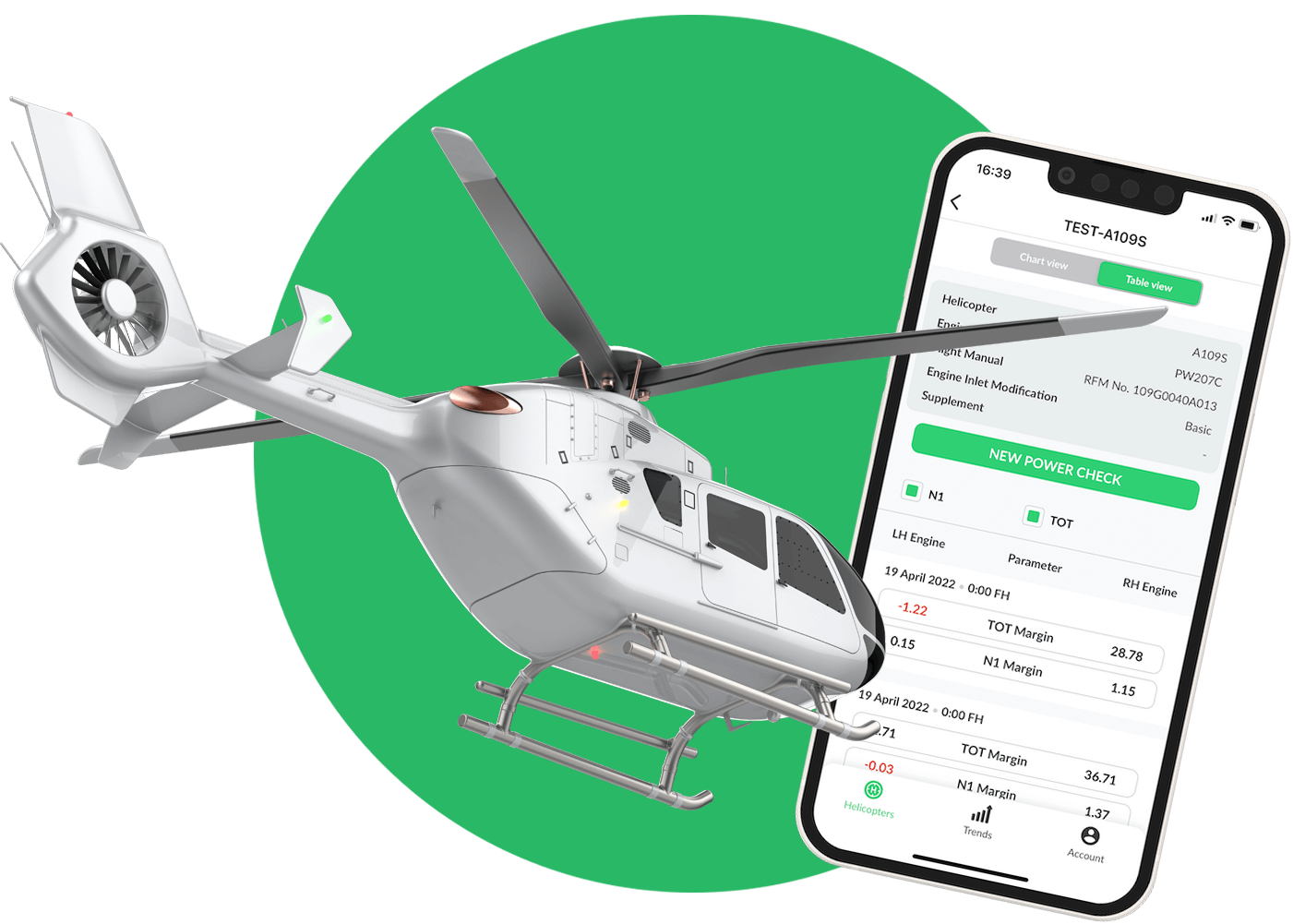
How can you avoid these problems using the Engine Continuous Trends Monitoring tool?
Engine condition trend monitoring (ECTM) is a valuable tool for avoiding helicopter engine faults. Here's how it can help:
1. Continuous Monitoring: ECTM involves the regular collection and analysis of engine performance data, including parameters such as temperatures, pressures, vibrations, and fuel consumption. By monitoring these trends over time, you can identify any deviations from normal operating conditions that may indicate the early stages of a potential fault.
2. Early Detection of Anomalies: ECTM allows you to establish baseline performance parameters for your engine. By comparing current data to these established baselines, you can quickly identify any abnormal trends or significant deviations. Early detection of anomalies enables you to take proactive measures to address the underlying issues before they escalate into serious engine faults.
3. Trend Analysis: ECTM involves analyzing long-term trends in engine performance data. By studying these trends, you can identify patterns or recurring issues that may be indicative of specific faults or degradation over time. This information helps in identifying potential problem areas and allows for targeted maintenance actions to be taken to prevent faults.
4. Condition-Based Maintenance: ECTM enables a shift from traditional calendar-based maintenance to condition-based maintenance. Instead of performing maintenance tasks at fixed intervals, maintenance actions can be scheduled based on the actual condition of the engine. This approach maximizes operational availability while ensuring that maintenance tasks are performed when they are most needed, minimizing the risk of faults.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making: ECTM provides valuable insights into the health and performance of the engine. By analyzing the collected data, you can make informed decisions regarding operational procedures, maintenance schedules, and potential corrective actions. This data-driven decision-making approach allows for proactive management of the engine's condition and minimizes the chances of unexpected faults.
By implementing an effective engine condition trend monitoring program, operators can detect early warning signs of potential engine faults, address issues proactively, and optimize maintenance activities. This leads to improved reliability, enhanced safety, and increased overall operational efficiency of helicopter engines.